
Preventive maintenance, also known as planned maintenance, is a process that consists in intervening on a machine at at regular intervals or according to predefined criteria. This business process is opposed to corrective maintenance, which consists in solving a problem when the breakdown occurs. Thus, the goal of preventive maintenance is to reduce the risk of failure, but also mitigate operating costs. In order to respond to this business process, SAP has implemented numerous functionalities within its PM (Plant Maintenance) / EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) module. Thus, let's discover through this article SAP PM - Preventive Maintenance.
SAP PM - Preventive maintenance: the basic principles
In summary, the process of preventive maintenance is to limit the risk and frequency of machine breakdowns. Through this, preventive maintenance allows to:
Thus, preventive maintenance allows the company to remain competitive in the market. Moreover, planning maintenance also allows to meet the requirements of the QMS (Quality Management System) and in particular the ISO standard. Finally, developing preventive maintenance increases customer satisfaction because stock and production shortages are avoided. At the same time, internal efficiency is also increased due to cost reduction, increased equipment life and improved working conditions.
SAP PM - Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance can be broken down into three main types:
Time-Based Maintenance
In this case, preventive maintenance activities are triggered after a period of time has passed. For example, every 2 months.
Performance-Based Maintenance
In this case, preventive maintenance activities are triggered once a certain performance level is reached. For example, every 2,000km.
Condition-Based Maintenance
In this case, preventive maintenance activities are triggered when a certain value has not been reached or has been exceeded. For example, the temperature has exceeded 65°C.
SAP PM - Preventive maintenance : the objects
As the explanations and definitions presented above are theoretical and general for each of the companies that have a maintenance department, let's see how it is articulated through the PM (Plant Maintenance) or EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) module.
In order to be able to execute business processes, SAP and its maintenance management module require various interconnected objects. These include:
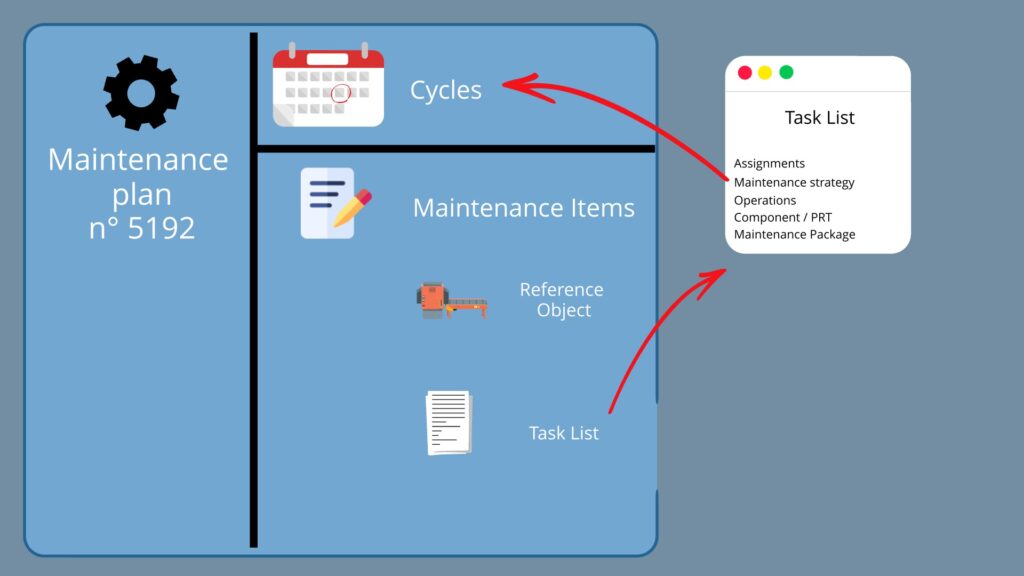
Now let's present each of the objects in detail.
Maintenance strategy
A Maintenance Strategy contains a chronological sequence of maintenance activities to be performed. We then talk about "Packages". Let's take the case of a Time-based maintenance for example. Thus, the Maintenance Strategy could represent the following chronological sequence: 2, 4, 6, 8 months, where each cycle represents a "Package".
Indeed, a Maintenance Strategy does not provide any information about the different activities (details, purpose, date...), but only chronological cycles. Moreover, a Maintenance Strategy is only to be used within the framework of a Strategy-based maintenance plan, which we will detail a little later in this article.
Maintenance task list
A Maintenance Task List contains a list of activities (also called operations), the materials needed to perform them and the various milestones. In addition to being useful in maintenance, Task Lists are also used in other areas such as QM (Quality Management) as an Inspection Plan. In general, Task Lists are intended to be integrated with the preventive maintenance process. They can also be used in the repair process. Indeed, it is possible to define standard operations to be carried out within the framework of certain breakdowns.
Finally, SAP distinguishes three different types of Task List that we will detail below.
Maintenance Item
A Maintenance Item simply allows you to describe the activities to be performed, contains the technical reference object (or reference objects via the object list), as well as the organizational data.
Maintenance Plan
The Maintenance Plan contains the different dates / cycles of interventions, as well as other planning parameters. In addition, it also contains one or more Maintenance Item(s). Then, it also contains the Call Object information (Order, Notification...).
Finally, SAP distinguishes three different types of Maintenance Plan categories, which we will detail below.
Single Cycle Plans are used when maintenance activities are to be performed at regular intervalsThis can be either time-based (every year) or performance-based (every 200 pulses). In this case, the insertion of a task list is optional.
Transaction: IP41
Maintenance Strategy Plans
Maintenance Strategy Plans are used in cases where maintenance activities are associated with different periods for the same planThis can be time-based (every 3,6,12 months) or performance-based (every 1000, 1200, 1800km). In this case, the insertion of a task list is mandatory.
Transaction: IP42
Multiple counter plans
Multiple Counter Plans are used when maintenance activities depend on several factors (every 100h, every 5h of operation, every 150km). In this case, the insertion of a task list is also optional.
Transaction: IP43
SAP PM - Preventive Maintenance: Time-Based Maintenance
In the context of time-based preventive maintenance, the dates are only based on the calendar. For example, one or more maintenance operations that must be performed every 3 months. In fact, there are two types of preventive maintenance: Time-Based Single Cycle Plan & Strategy Plan.
Time-Based Single Cycle Plan
Among the time-based preventive maintenance process, we find first of all the possibility single cycle plan. The latter implies that all maintenance operations must be carried out at regular time intervals.
Creation Maintenance Plan
In order to create a single cycle maintenance plan, you must use the IP41. In the "Maintenance plan cycle" tab, this is where the cycle of operations is indicated. In the example below, the maintenance operations should be carried out every 3 months (regular time intervals):

Time-Based Strategy Plan
The time-based preventive maintenance process also contains a second option: strategy plan. The latter allows maintenance operations to be carried out that depend on each other or that can be replaced.
In order to create a strategy maintenance plan, you must use the IP42. Unlike the previous IP41 transaction, SAP asks us here to specify the strategy to be used:

Maintenance Strategy
A Maintenance Strategy lists the different maintenance cycles (also called packages) in chronological order. In order to create a Maintenance Strategy, you must use the IP11. A maintenance strategy contains :

Packages and Task List
Reminder: as part of a maintenance strategy plan, the assignment of a task list is mandatory.
Thus, it is necessary here to assign for each of the operations of the task list, the cycle that corresponds to it:

Creation Maintenance Plan
Once the maintenance strategy is created and the task list is modified, it is possible to create the strategy maintenance plan:

SAP PM - Preventive Maintenance: Performance-Based Maintenance
Performance-based preventive maintenance sets intervention dates based solely on performance values. For example, one or more maintenance operations that must be performed every 10 km). As before, there are two types of preventive maintenance: Performance-Based Single Cycle Plan & Strategy Plan.
Performance-Based Single Cycle Plan
Unlike time-based single cycle plans, performance-based single cycle plans require several prerequisites. Indeed, it is necessary first of all to assign the counter to the reference object (equipment or functional location). To do this, the first step is to create a feature that refers to the counter, such as "Operating Hours":

Create Characteristic
To maintain a feature, you must use the CT04. For more information about the features, please visit this article https://keyusertraining.com/sap-systeme-de-classification/.
Creation Measuring Point
Then, once the characteristic is created, the Measuring Point (also called counter) must be created. In order to create the Measuring point, you have to use the IK01. Then it is necessary to assign the characteristic to the Measuring Point :

Creation Maintenance Plan
Then comes the creation of the single cycle maintenance plan. To do this, the same transaction must be used as for the creation of the time-based single cycle maintenance plan: IP41. The major difference is in the "Maintenance plan cycle" tab, where it will be necessary to enter the counter number (Measuring Point):

Performance-Based Strategy Plan
As with the time-based preventive maintenance process, the performance-based process also has a second option: strategy plan. The latter allows maintenance operations to be carried out that are dependent on each other or that can replace each other, but this time linked to performance.
Maintenance Strategy
As before, the first step is to create the maintenance strategy (transaction IP11). On the other hand, this time, the packages no longer correspond to time cycles but to performance cycles (in this case operating hours):

Packages and Task List
Reminder: as part of a maintenance strategy plan, the assignment of a task list is mandatory.
Here we have to reproduce the same operation as before, i.e. assign each operation of the task list to one or more packages present in the strategy:

Creation Maintenance Plan
Finally, it is then possible to create the maintenance plan via the transaction IP42:

SAP PM - Preventive maintenance: time-based and performance-based maintenance
In the context of a preventive maintenance process based on time and performance, the calculation of dates is done according to the calendar as well as the performance. It is indeed a combination of time-based and performance-based options.
Basic Multiple Counter plan
Using the multiple counter plan, it is possible to create cycles with different dimensions, for example every 5 months, every 200 hours of operation. In fact, the multiple counter plan allows to combine the dimensions of time and performance within the same maintenance plan.
In addition, to create a multiple counter plan, you must use the IP43. In this case, you can create the cycles directly within the maintenance plan:

SAP PM - Preventive Maintenance: Condition-Based Maintenance
The most recent preventive maintenance process, condition-based maintenance, allows maintenance to be performed when the actual state of a technical object differs from the intended state.
While the time-based process allows to trigger maintenance operations once a certain time has been reached, the performance-based process once a certain counter has been reached, the condition-based process can trigger maintenance operations in the following example cases:
Therefore, we ask you to fill in the following information for each of the desired technical objects a target value as well as a value range containing the minimum and maximum limit.
Would you like to improve your SAP skills? You can access our free training courses, or opt for our premium "Beyond the Horizon" (SAP beginners) or "Expert Training Center" (advanced) courses.

Pierre Balbinot
SAP functional consultant, EAM (Enterprise Asset Management) and PP (Production Planning) expert.












